

Variable capacitors normally are not marked with their value.

2 (L is inductance in µh, C is capacitance in µf and f is frequency in MHz.) It is just as useful for measuring unknown capacitors. Just temporarily connect a capacitor with a known value in parallel with the coil to be tested, measure the resonant frequency and use the formula L = 1/(2πf) 2 C or use the graph in The ARRL Handbook. Be sure to turn off the high voltage first! A GDO has other uses you might not think of. A GDO can sniff out spurious resonances in the tank circuit of a high-power vacuum-tube RF amplifier. A GDO is also perfect for tuning the traps to resonance on a multi-band Yagi. Since the parasitic elements have no feedpoint, you can t measure the resonant frequency the normal way, with an SWR meter.

An example is measuring the parasitic elements of a beam antenna. This no connection measurement capability is handy for other purposes as well. Just bring the coil close to the tuned circuit s coil and tune the GDO while watching for a dip in its meter reading. The external coil allows you to measure the frequency of a tuned circuit without any electrical connection to it. A GDO is a tunable oscillator with the coil mounted outside of the chassis. Amateurs have been using grid-dip oscillators (GDOs) at least since While these days they no longer have a vacuum-tube grid to dip, the name seems to have stuck. It still works, although the coil socket has become intermittent over the years, which makes it a bit frustrating to use. It weighs over 2 pounds and must be plugged into the wall to obtain power for its 6AF4 vacuum tube.
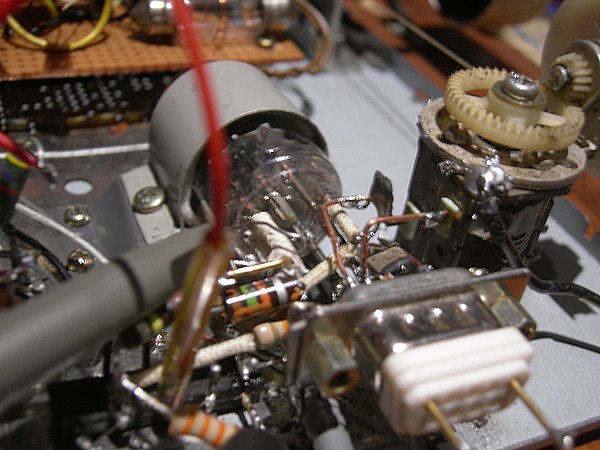
It s an Eico model 710 that covers 0.4 to 250 MHz with 8 plug-in coils. Istill have my first grid-dip oscillator, purchased at a flea market about 30 years ago. 1 By Alan Bloom, N1AL A Modern GDO The Gate Dip Oscillator Building an RF circuit? Use an updated version of an indispensable and legendary piece of equipment to test it the dipper.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
